The Complete Science of Hypochlorous Acid
Nature's Most Powerful Antimicrobial: Comprehensive guide to the molecular structure, biological production, antimicrobial mechanisms, and clinical applications of hypochlorous acid (HOCl).
Evidence-Based Analysis:
- • 200+ Peer-Reviewed Studies
- • FDA & EPA Approved Applications
- • Clinical Trial Data & Research
- • Molecular Mechanism Analysis
Molecular Chemistry
Understanding HOCl at the Molecular Level
Chemical Formula: HClO
Hypochlorous acid exists as a simple triatomic molecule with hydrogen, chlorine, and oxygen atoms in equilibrium with hypochlorite ion (ClO⁻)
Oxidizing Properties
With an oxidation potential of +1.48V, HOCl is one of the most potent oxidizing agents in biological systems, surpassing hydrogen peroxide (+1.31V)
pH-Dependent Equilibrium
At pH 6.5-7.5, ~80% exists as HOCl (most antimicrobial form). At higher pH, it shifts to less effective hypochlorite ion (ClO⁻)
Immune System Production
How Your Body Naturally Produces HOCl
Every day, your immune system produces approximately 1-2 grams of hypochlorous acid to defend against pathogens and maintain health.
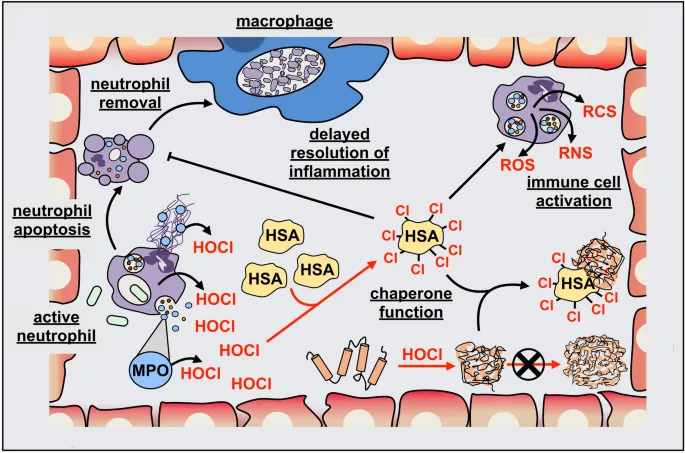
Neutrophil Activation
White blood cells (neutrophils) detect pathogens and migrate to infection sites, representing 50-70% of circulating white blood cells.
Myeloperoxidase Enzyme
Activated neutrophils release myeloperoxidase (MPO), a heme-containing enzyme that catalyzes HOCl formation from H₂O₂ and Cl⁻ ions.
Respiratory Burst
The "oxidative burst" generates reactive oxygen species including HOCl, consuming oxygen at rates 10-20x normal metabolism.
Pathogen Elimination
HOCl rapidly penetrates microbial cell walls and destroys essential proteins, DNA, and cellular components within seconds.
Tissue Protection
Specialized enzymes like catalase and peroxidases help neutralize excess HOCl, preventing tissue damage while maintaining antimicrobial activity.
Resolution Phase
After pathogen clearance, anti-inflammatory signals promote tissue repair and return immune cells to surveillance state.
Antimicrobial Science
Multi-Target Pathogen Destruction Mechanisms
Cell Membrane Disruption
HOCl oxidizes phospholipids and membrane proteins, causing immediate cell wall permeabilization and osmotic lysis
Protein Denaturation
Reacts with sulfhydryl groups (-SH) and amino groups in essential enzymes, permanently disrupting protein structure and function
Nucleic Acid Damage
Oxidizes purine and pyrimidine bases in DNA/RNA, preventing replication and transcription processes
Metabolic Disruption
Inactivates key metabolic enzymes including those in glycolysis, respiratory chain, and ATP synthesis pathways
Clinical Evidence
Research-Proven Medical Applications
Decades of clinical research demonstrate HOCl's therapeutic potential across multiple medical specialties
50+ studies show accelerated healing, reduced infection rates, and improved tissue regeneration in chronic wounds, burns, and dermatological conditions.
Clinical trials demonstrate efficacy in treating dry eye syndrome, conjunctivitis, and post-surgical infections with zero adverse effects.
Randomized controlled trials show significant reduction in periodontal pathogens, gingivitis improvement, and enhanced post-surgical healing.
Hospital studies demonstrate 99.99% pathogen elimination including MRSA, VRE, C. difficile, and SARS-CoV-2 within 30-60 seconds.
Nebulized HOCl studies show promise for respiratory tract infections, sinusitis, and as adjunctive therapy for chronic respiratory conditions.
Veterinary trials confirm safety and efficacy for animal wound care, skin conditions, and environmental disinfection without toxicity concerns.
Safety & Toxicology
Exceptional Safety Profile: Why HOCl is Different
Non-Toxic at Therapeutic Concentrations
LD50 >10,000 mg/kg (essentially non-toxic). Safe for direct skin, eye, and oral contact at recommended concentrations (10-100 ppm)
No Harmful Byproducts
Breaks down naturally to water (H₂O) and trace amounts of salt (NaCl). No formation of toxic chlorinated organic compounds or trihalomethanes
Non-Sensitizing & Non-Irritating
Patch testing shows 0% sensitization rate. No respiratory irritation even with chronic exposure. Compatible with all skin types including sensitive skin
Regulatory Approvals
FDA cleared for wound care, eye care, and food contact surfaces. EPA registered as hospital disinfectant. USDA approved for organic food processing
Production Technology
Medical-Grade HOCl Production Methods
Understanding how medical-grade HOCl is produced ensures quality, safety, and therapeutic efficacy
Electrochemical Generation
Controlled electrolysis of dilute salt solutions using specialized electrodes produces pure HOCl with precise pH and concentration control.
pH Optimization
Maintaining pH 5.0-6.5 ensures >95% hypochlorous acid vs. hypochlorite ion, maximizing antimicrobial potency and stability.
Electrode Technology
Medical-grade systems use platinum-coated titanium electrodes with precise current control to prevent harmful byproduct formation.
Quality Control Testing
Each batch undergoes pH verification, free chlorine analysis, microbial testing, and stability assessment to ensure therapeutic standards.
Antimicrobial Comparison
HOCl vs. Traditional Antimicrobials: Scientific Comparison
Superior Efficacy
100x more effective than sodium hypochlorite (bleach) at equivalent pH. Maintains activity in presence of organic matter unlike alcohol-based sanitizers
Faster Action
Achieves 6-log reduction (99.9999%) of pathogens in 15-30 seconds compared to 1-5 minutes required by conventional disinfectants
Broader Spectrum
Effective against bacteria, viruses, fungi, spores, and biofilms. No known resistance mechanisms unlike antibiotics and conventional biocides
Environmental Compatibility
Biodegradable with no environmental accumulation. No contribution to antibiotic resistance or ecological disruption
Future Research
Emerging Applications & Research Frontiers
Current clinical trials and research directions for hypochlorous acid applications
Investigating HOCl role in enhancing immune surveillance and reducing tumor-associated infections in immunocompromised patients.
Research on HOCl ability to cross blood-brain barrier and modulate neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
Clinical trials examining HOCl therapeutic potential in rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Development of rapid-deployment HOCl systems for emerging infectious disease control and biodefense applications.
Frequently Asked Questions: HOCl Science
Expert answers to common questions about hypochlorous acid science and applications
How does HOCl differ from other forms of chlorine?
HOCl is the neutral, molecular form of "available chlorine" that exists in equilibrium with hypochlorite ion (ClO⁻). At physiological pH (7.4), about 20% exists as HOCl and 80% as ClO⁻. However, HOCl is 80-100 times more antimicrobial than ClO⁻ because its neutral charge allows it to easily penetrate negatively charged microbial cell walls. Other chlorine forms like chloramine (NH₂Cl) and chlorine dioxide (ClO₂) have different chemical properties and mechanisms of action.
Can bacteria develop resistance to HOCl?
Bacterial resistance to HOCl is extremely rare and unlikely due to its multi-target mechanism of action. Unlike antibiotics that target specific cellular processes (allowing resistance mutations), HOCl simultaneously attacks cell membranes, proteins, DNA, and metabolic enzymes. This would require multiple simultaneous mutations that would likely be lethal to the organism. Additionally, HOCl is part of the natural immune system, so organisms have evolved alongside this antimicrobial for millions of years.
What concentration of HOCl is optimal for different applications?
Optimal concentrations vary by application: Wound care: 10-50 ppm, Skin conditions: 20-80 ppm, Oral rinse: 10-30 ppm, Surface disinfection: 50-200 ppm, Food processing: 10-60 ppm. Higher concentrations are not necessarily better and may cause unnecessary chlorine odor or taste. The key is maintaining proper pH (5.0-6.5) to ensure maximum HOCl percentage regardless of total chlorine concentration.
How long does HOCl remain stable and active?
HOCl stability depends on several factors: pH (stable at 5.0-6.5), temperature (degrades faster above 25°C), light exposure (UV light accelerates decomposition), organic load (consumes available chlorine), and container material (some plastics catalyze degradation). Properly produced and stored HOCl can maintain >90% activity for 6-12 months in appropriate containers under ideal conditions. Fresh generation provides maximum potency.
Is there any difference between naturally produced and synthetic HOCl?
Chemically, there is no difference between HOCl produced by white blood cells and medical-grade electrochemically produced HOCl. Both have identical molecular structure, oxidation potential, and antimicrobial mechanisms. However, the body produces HOCl in localized bursts at very high concentrations (millimolar levels), while commercial HOCl provides sustained lower concentrations (micromolar levels). The advantage of synthetic HOCl is precise control over pH, concentration, and purity without inflammatory byproducts.
What does current research say about HOCl and immune system modulation?
Research shows HOCl has complex immunomodulatory effects beyond direct antimicrobial action. It can enhance T-cell activation, improve antigen presentation, and promote tissue repair signaling. Studies indicate HOCl may help rebalance overactive immune responses in autoimmune conditions while supporting immune function in immunocompromised states. This dual action makes it valuable for conditions involving both immune dysfunction and infection risk, such as chronic wounds or post-viral syndromes.
Experience the Science of HOCl
Ready to experience medical-grade hypochlorous acid benefits?
Our S2Y Smart HOCl Care Cup brings laboratory-grade quality to your home.
Medical-grade electrodes • pH optimization • Quality assured • 30-day guarantee
Additional Scientific Resources
Research Library
Access our curated collection of peer-reviewed HOCl studies
Browse Research Articles →


